Procedures

Preventive Cardiology
Clinic visits focused on lowering your risk of heart disease through lifestyle changes, medications, and monitoring of blood pressure, cholesterol, weight, and other risk factors.

Consultative Cardiology
A visit with a heart specialist to evaluate symptoms (such as chest pain, shortness of breath, or palpitations), review test results, and recommend further testing or treatment.
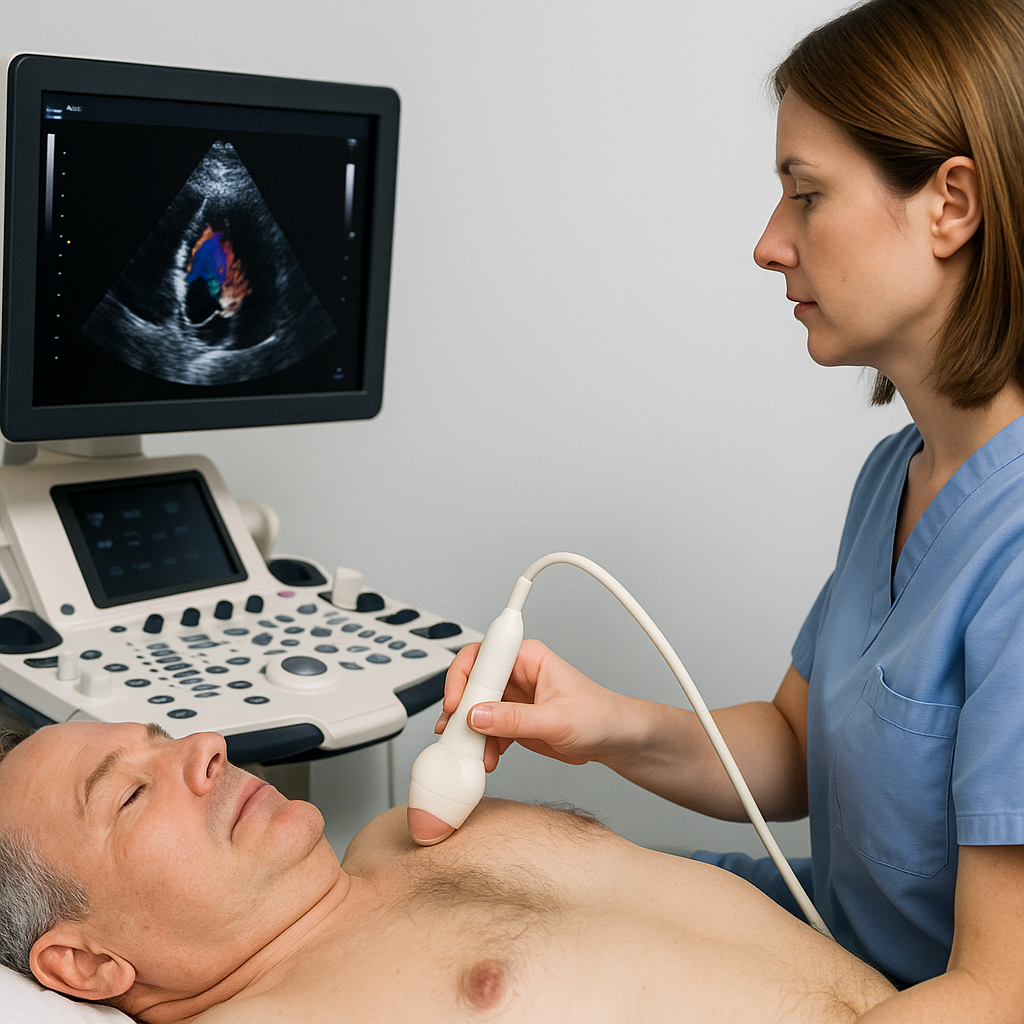
Echocardiogram
An ultrasound of the heart that uses sound waves to create moving pictures of the heart’s chambers, valves, and pumping function. Noninvasive and uses no radiation.
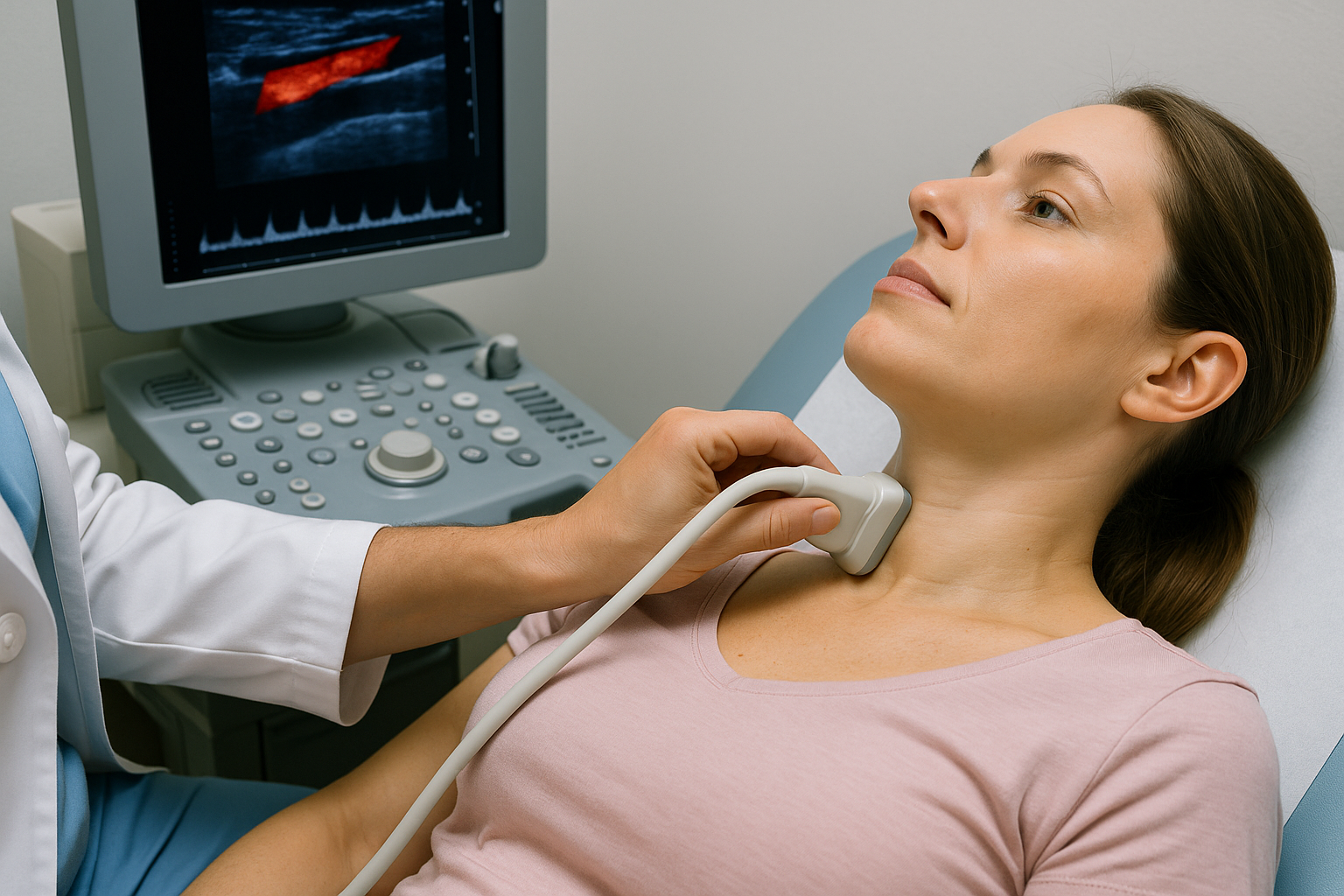
Peripheral Vascular Ultrasound
Ultrasound of the arteries and veins outside the heart (often in the neck, abdomen, or legs) to look for narrowing, blockages, or blood clots. Noninvasive and uses no radiation.
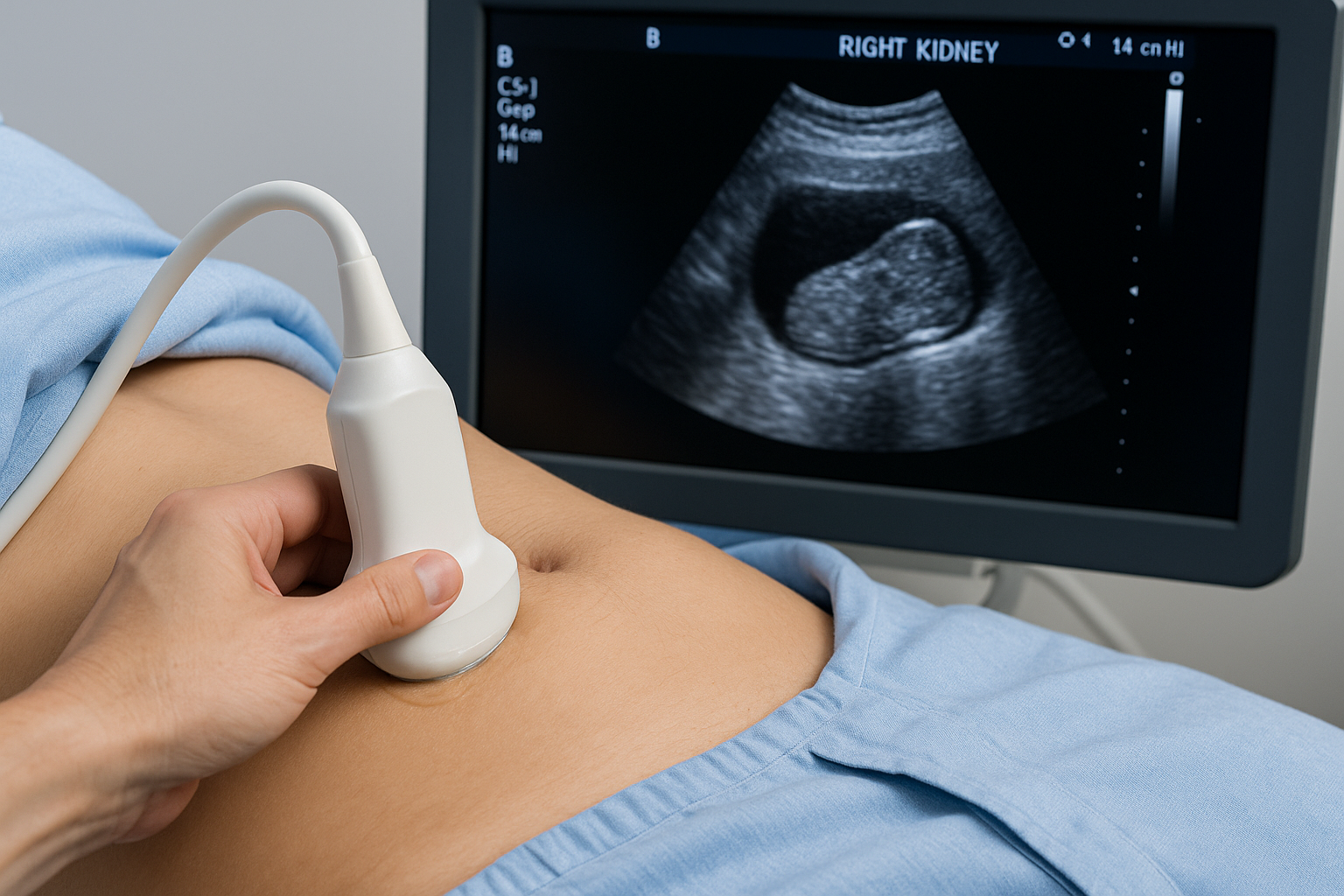
Renal
Ultrasound of the kidney (renal) arteries to check for narrowing that can affect blood pressure and kidney function. Gel is placed on the abdomen and a Doppler probe measures blood flow.
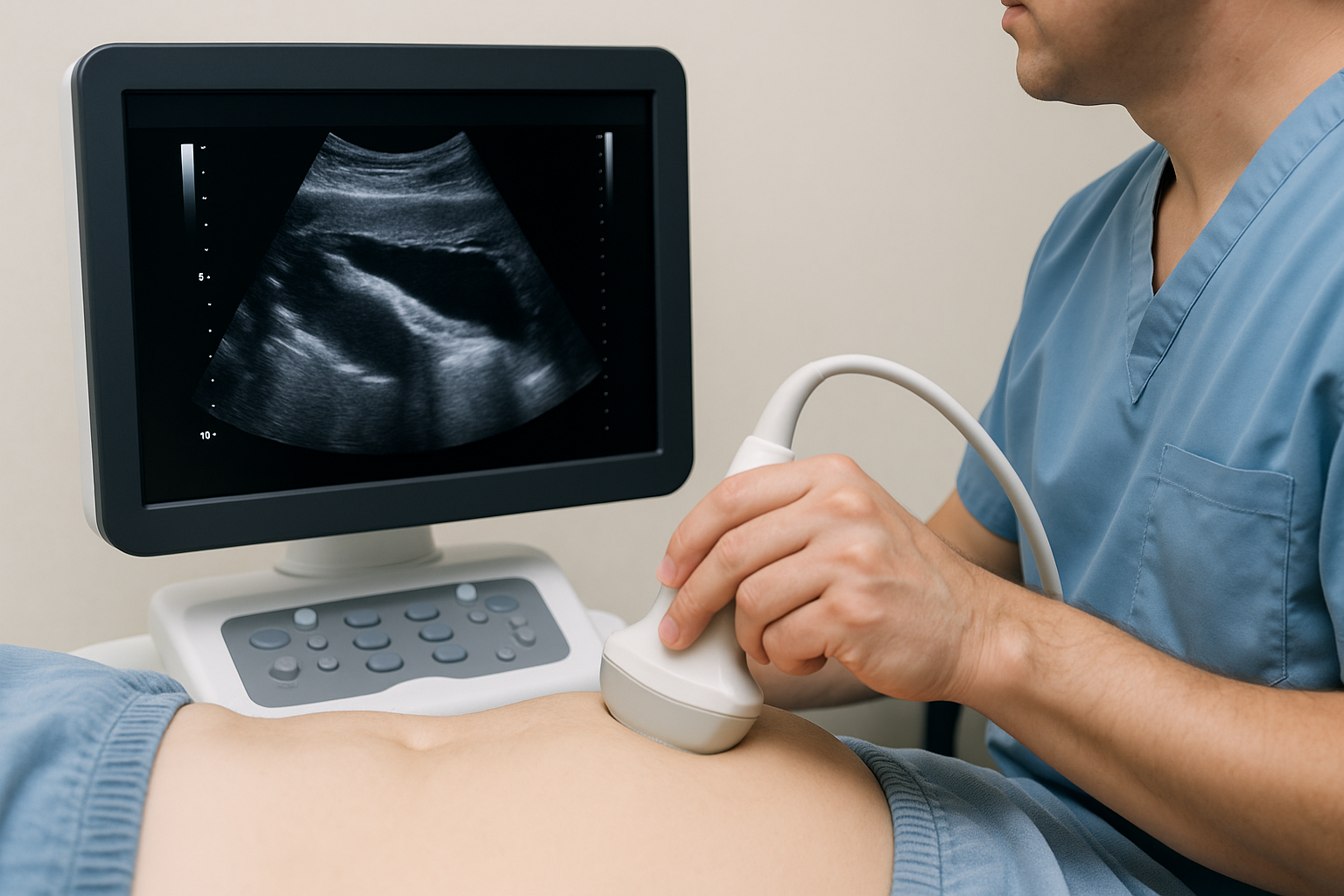
Abdominal Aortic Ultrasound
Ultrasound of the main artery in the abdomen (aorta) to look for bulging (aneurysm) or narrowing. Noninvasive, painless, and uses no radiation.
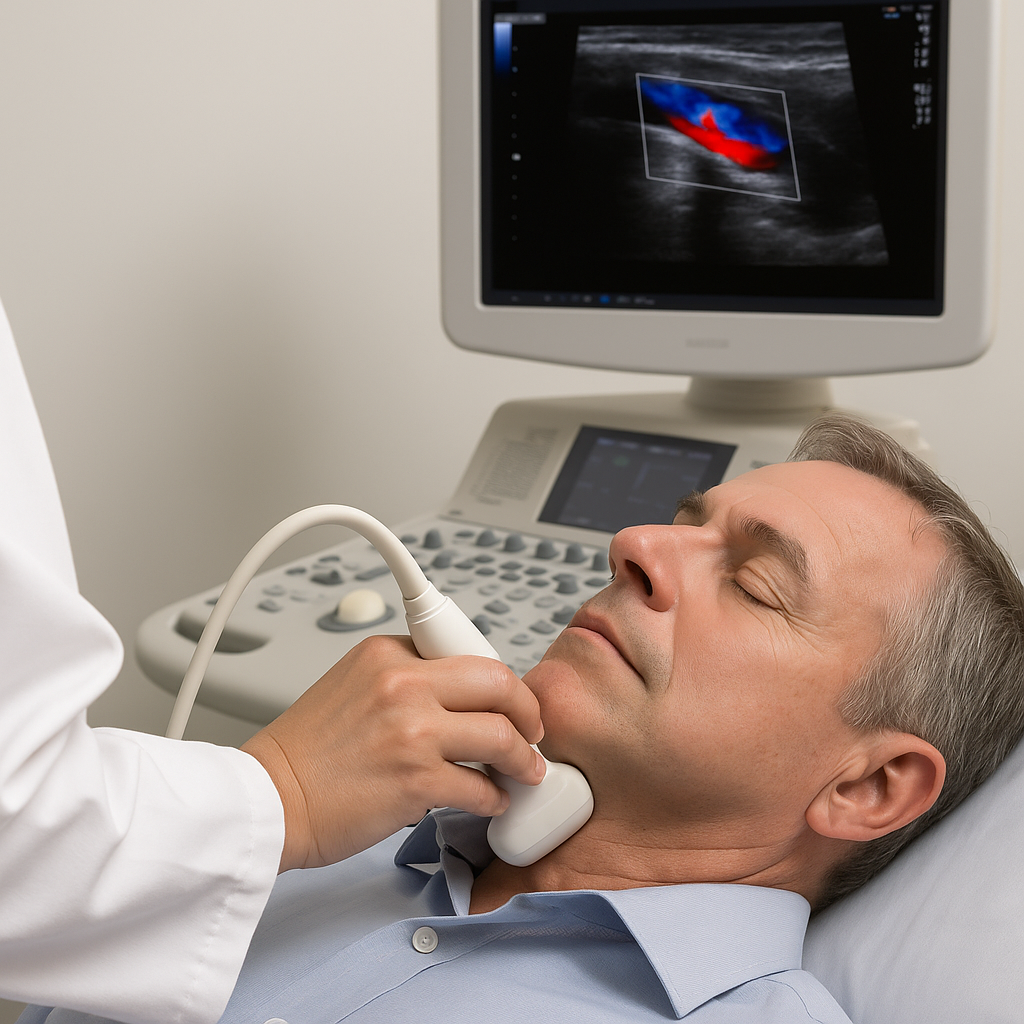
Carotid
Ultrasound of the neck arteries (carotids) that supply blood to the brain, used to check for plaque buildup and narrowing that can increase stroke risk.
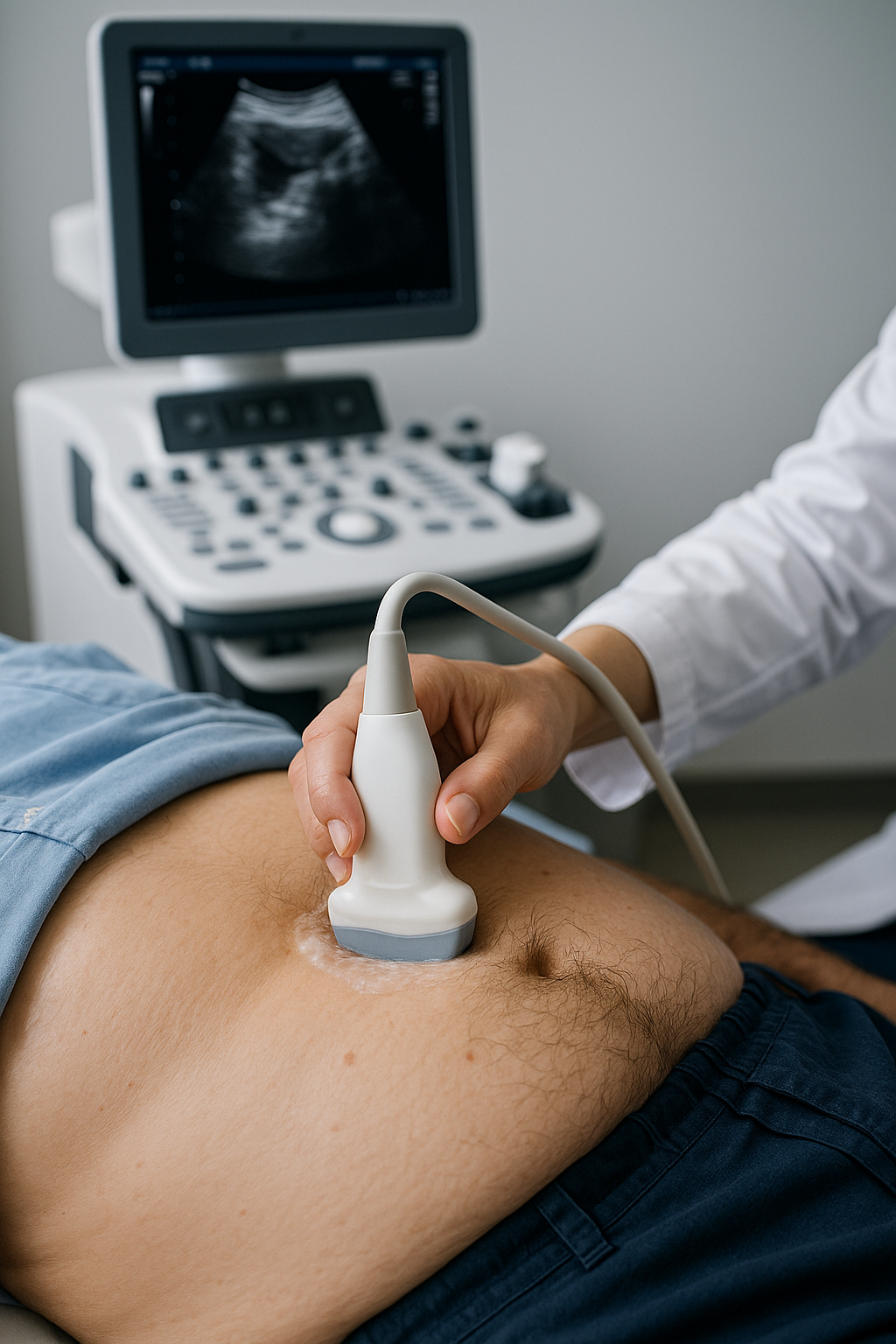
Mesenteric
Ultrasound of the intestinal (mesenteric) arteries to look for narrowing that reduces blood flow to the intestines and may cause abdominal pain, especially after eating. Gel is placed on the abdomen and a Doppler probe measures blood flow. Noninvasive, no radiation; fasting is often recommended for clearer images.
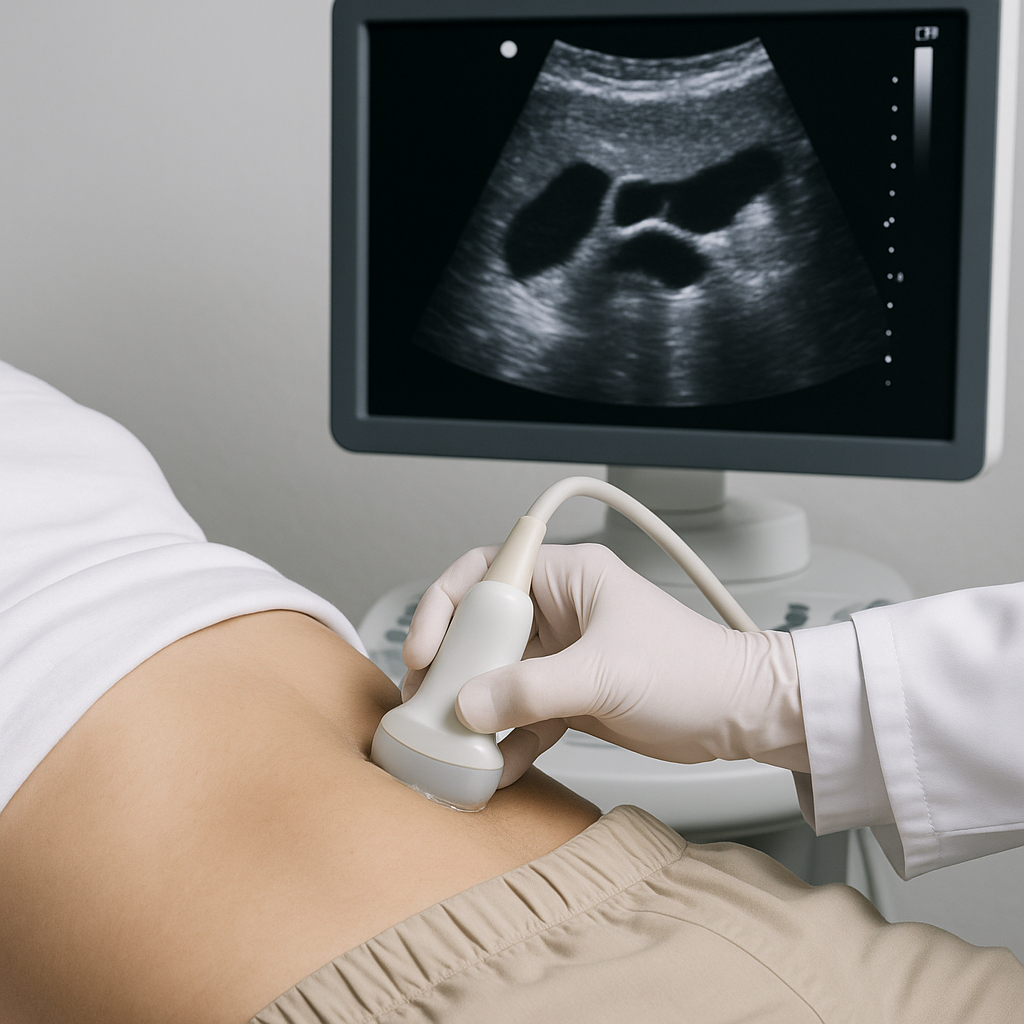
Celiac
Ultrasound of the celiac artery, which supplies blood to the stomach, liver, and spleen, to check for narrowing or blockage. Gel is placed on the upper abdomen and a Doppler probe measures blood flow. Noninvasive, no radiation; fasting is often recommended for clearer images.
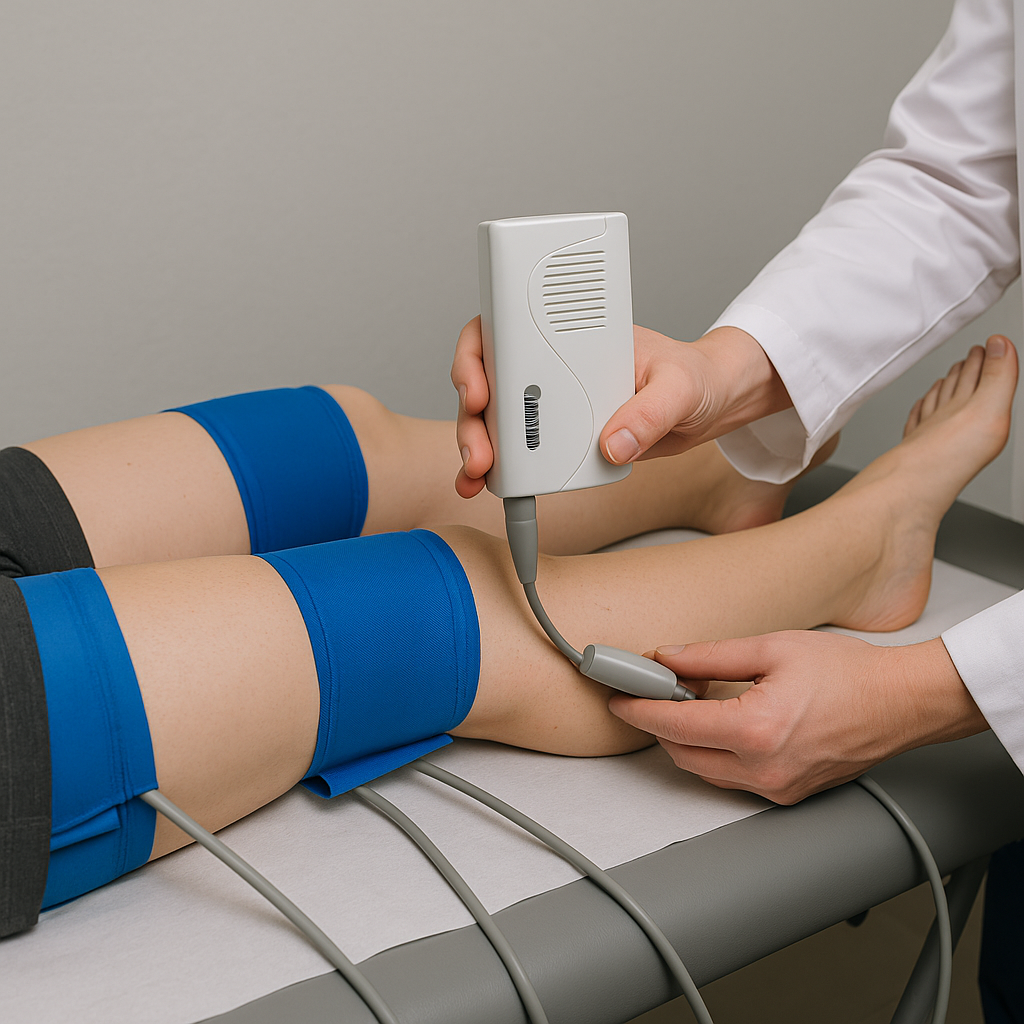
Leg Segmental Pressures
A circulation test that uses blood pressure cuffs at several levels on the legs and a Doppler probe to compare pressures from thigh to ankle. It helps locate narrowed or blocked arteries that may cause leg pain with walking.
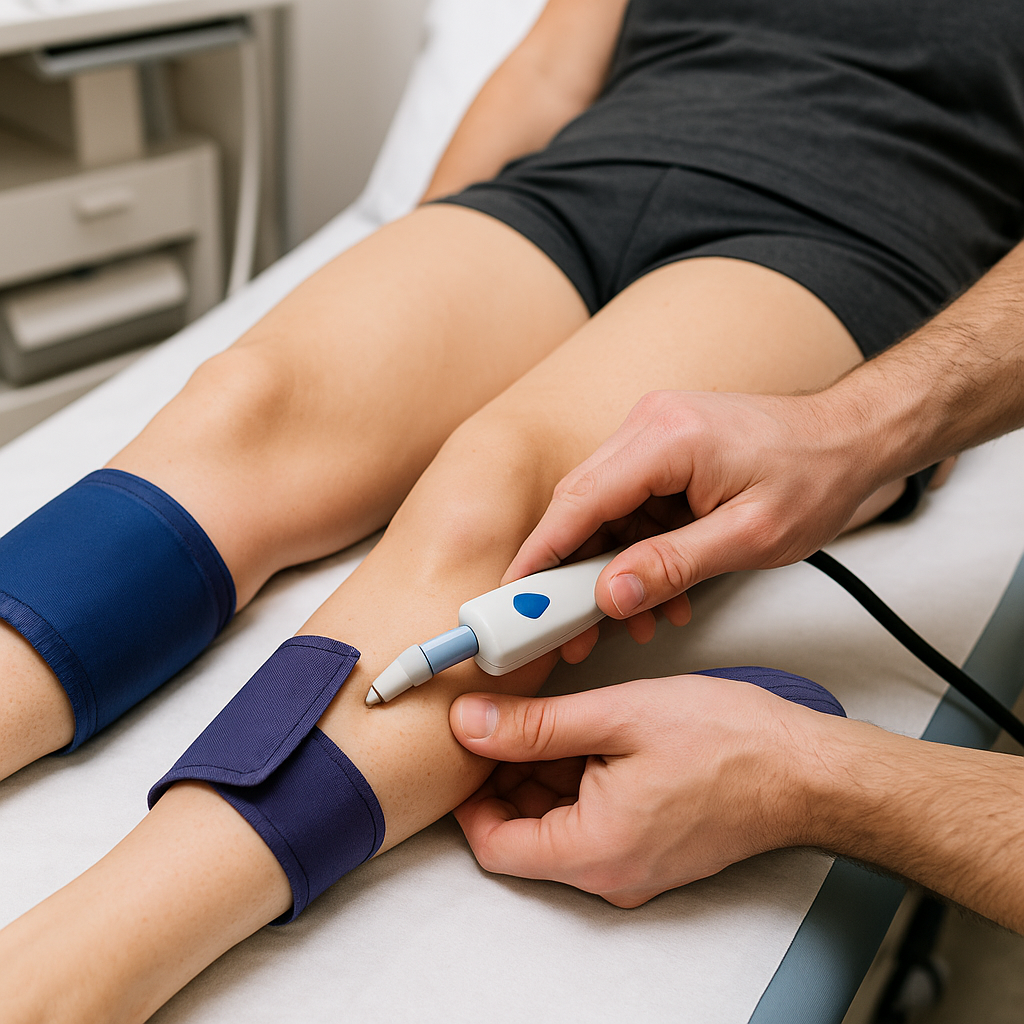
ABI (Ankle-Brachial Index)
A simple circulation test that compares blood pressure in your ankles to blood pressure in your arms to check for peripheral artery disease (poor blood flow to the legs). Done with cuffs and a Doppler probe; noninvasive and uses no radiation.
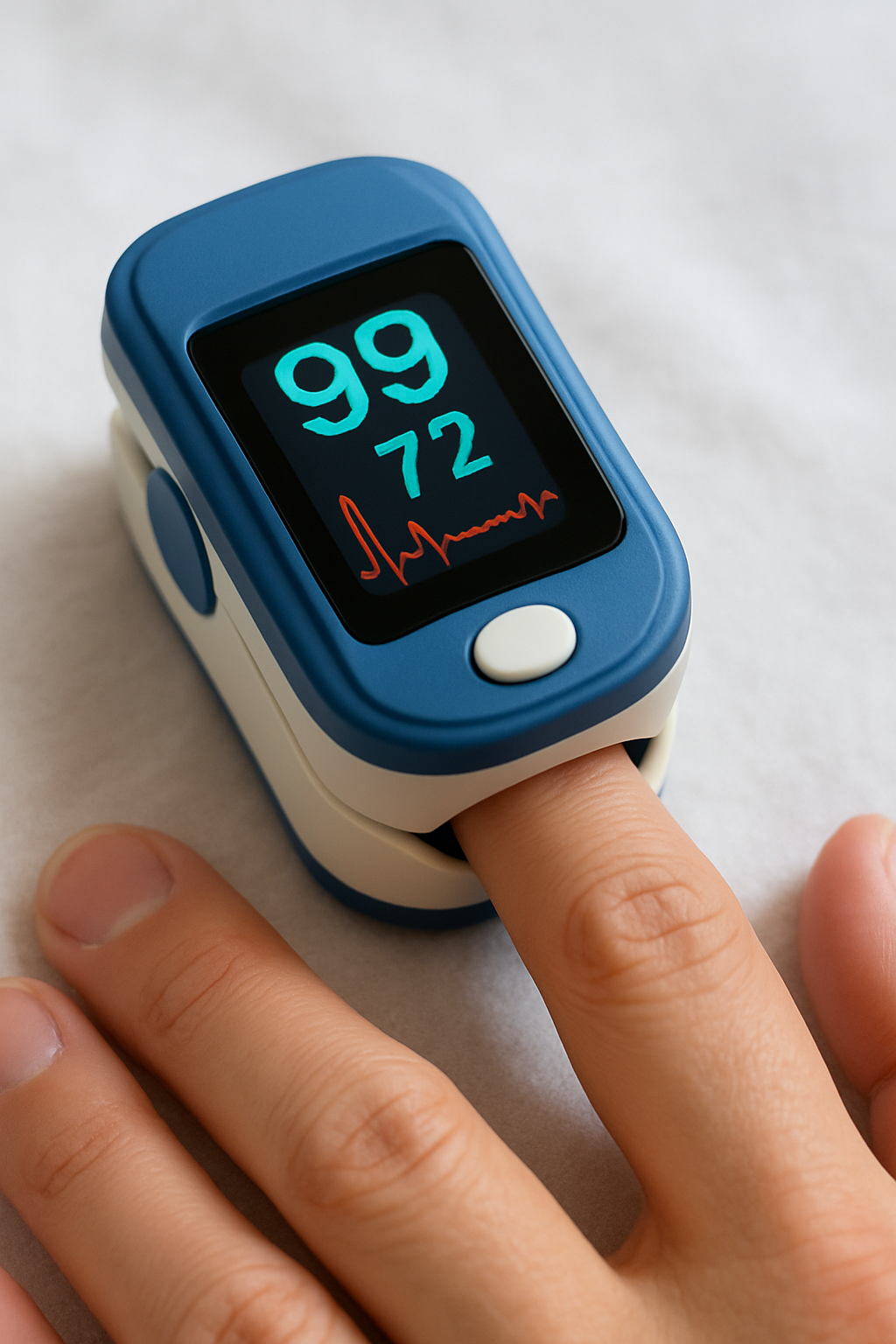
Pulse Oximetry
A quick, noninvasive test that uses a small sensor on your finger, toe, or ear to measure blood oxygen level and pulse rate. Uses light, not needles, and gives results in seconds.
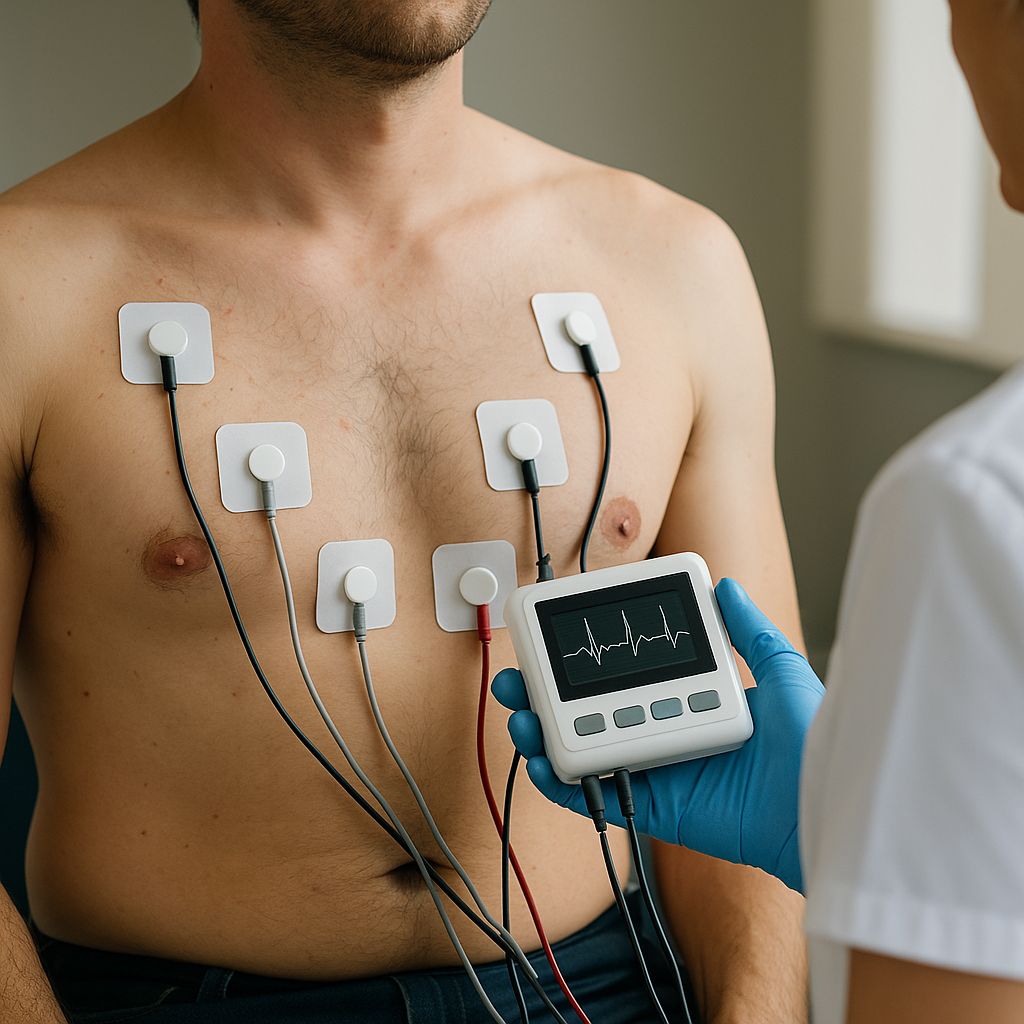
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG)
A quick, painless test that records the heart’s electrical activity using small stickers (electrodes) on the chest, arms, and legs. It helps detect abnormal heart rhythms, prior heart attacks, and other heart problems.
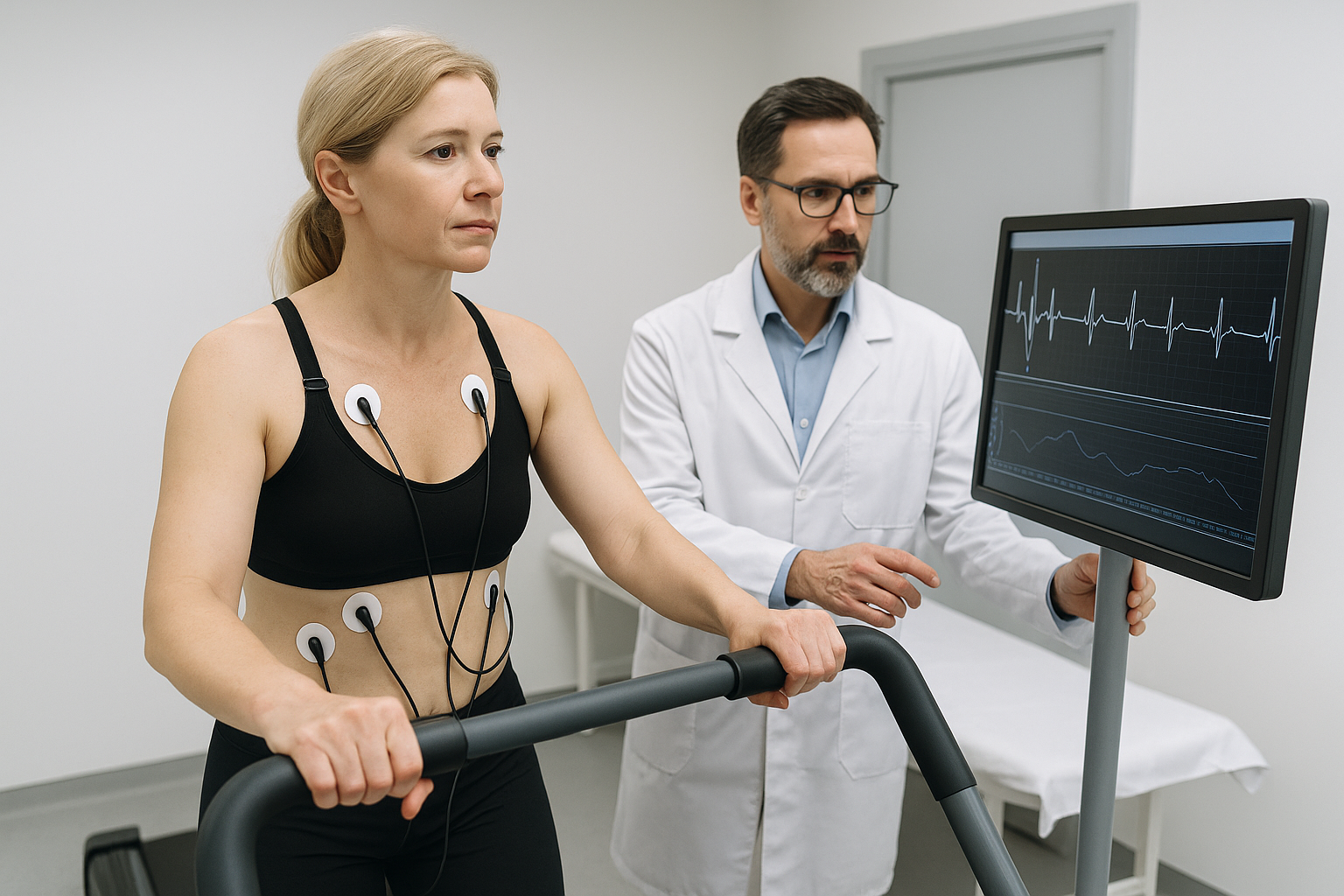
Simple Stress Test
A monitored walking test on a treadmill while your heart rhythm, heart rate, and blood pressure are recorded. Shows how well your heart handles exercise and can reveal reduced blood flow to the heart.
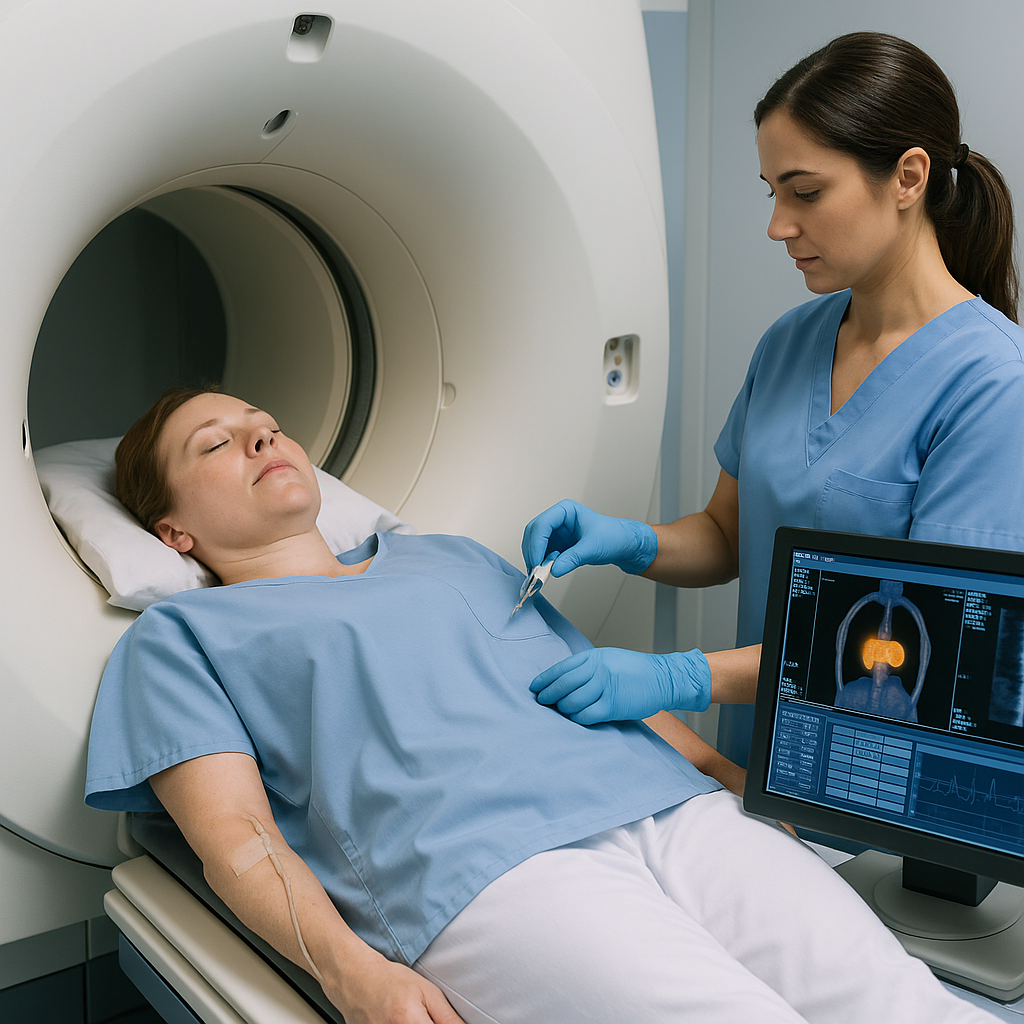
Cardiac Positron Emission Study (PET)
A heart imaging test that uses a small amount of radioactive tracer and a special camera to show blood flow to the heart muscle at rest and with stress. Helps find blocked arteries and measure how well the heart is working; involves an IV and low-dose radiation.
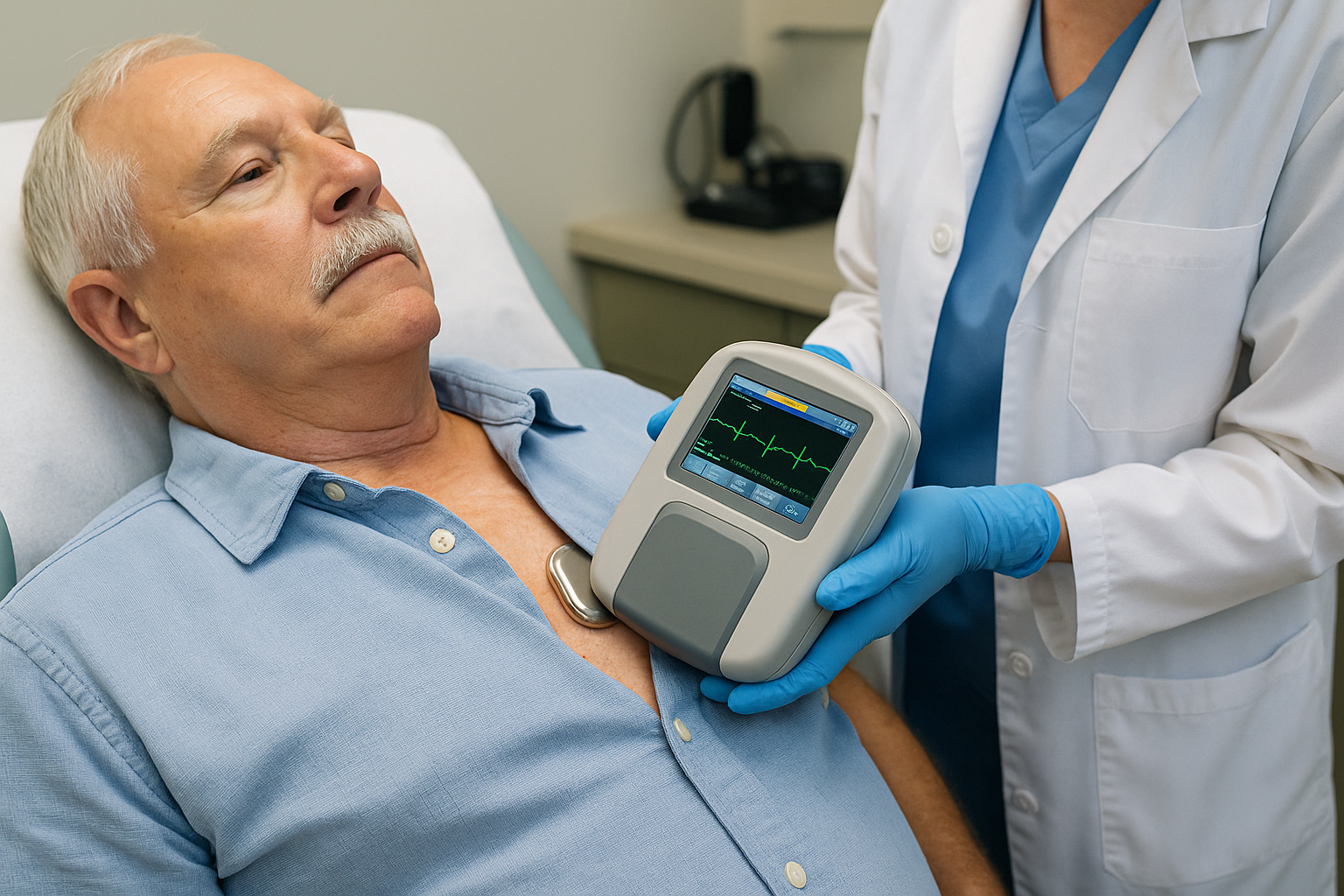
Pacemaker Interrogation
A check-up of your pacemaker using a special computer placed over your chest (no needles) to read and adjust settings, check battery life, and review stored heart rhythm data.
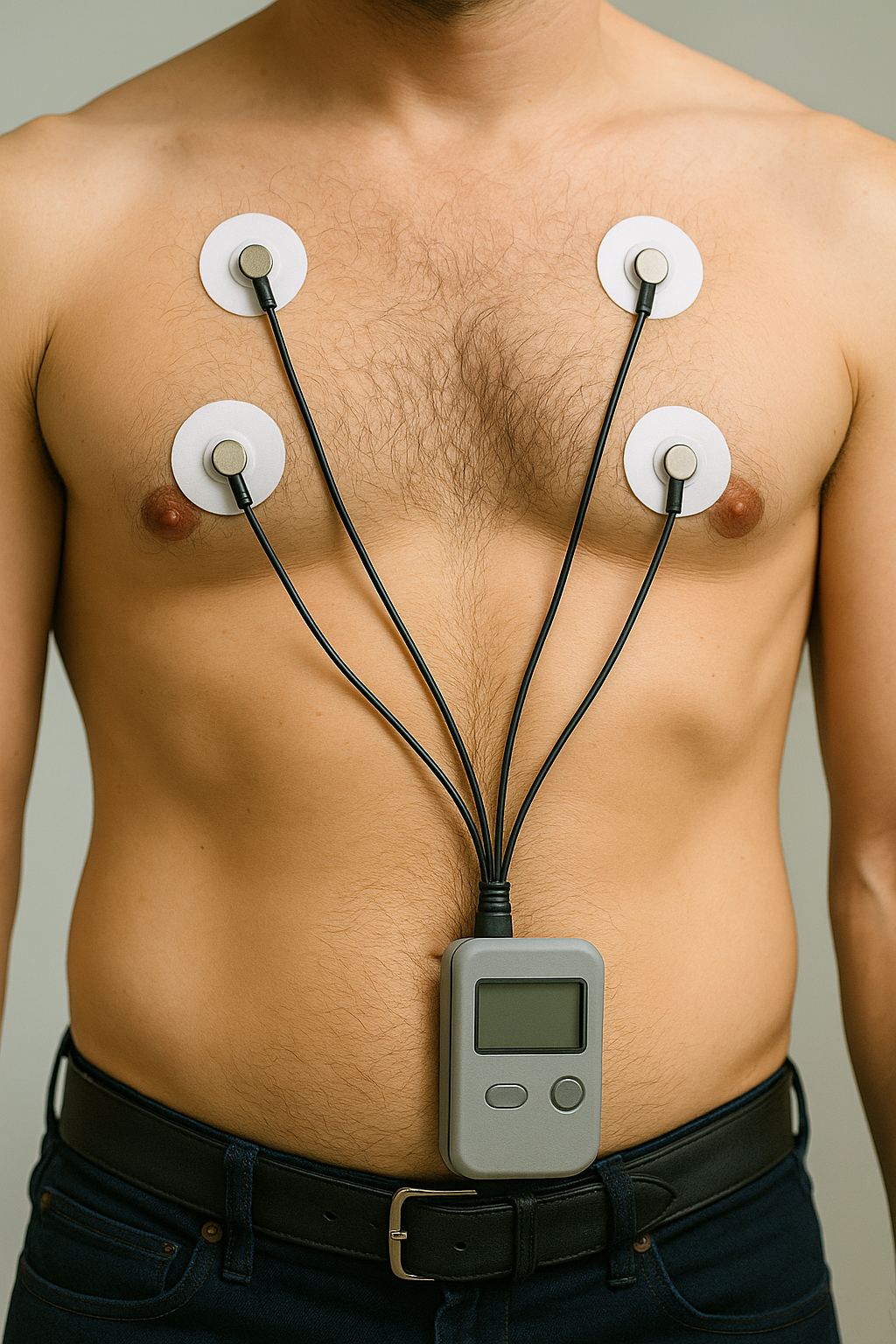
Holter Monitor
A small, portable heart monitor worn for 24–48 hours (or longer) to continuously record your heart rhythm during normal activities. Uses chest stickers connected to a recorder; painless and noninvasive.
